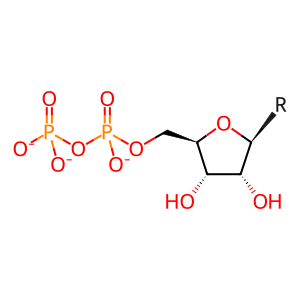
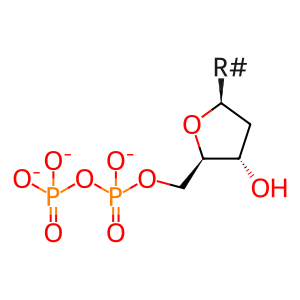
Reaction: RNR (M1M2) reduces nucleotide diphosphates to deoxynucleotide diphosphates (glutaredoxin)
- in pathway: Interconversion of nucleotide di- and triphosphates
Ribonucleotide reductase (RNR (M1M2)) catalyzes the reduction of adenine, guanine, cytidine, and uridine ribonucleoside 5'-diphosphates (NDPs) to form the corresponding deoxyribonucleoside 5'-diphosphates, coupled to the oxidation of glutaredoxin (Eklund et al. 2001). The enzyme complex is cytosolic (Pontarin et al. 2008). The form of ribonucleotide reductase annotated here is a tetramer of two large (M1) and two small (M2) subunits (Zhou et al. 2005). Expression of RNR (M1M2) is confined to the S phase of the cell cycle by restriction of the expression of the M2 gene and by degradation of the M2 gene product at the end of S phase (reviewed by Nordlund and Reichard 2006). The overall activity of the enzyme is regulated allosterically: ATP binding is stimulatory while dATP binding is inhibitory (Reichard et al. 2000).
The reducing equivalents needed for ribonucleotide reductase activity can be provided by either of two small proteins, glutaredoxin or thioredoxin (Holmgren 1989; Sun et al. 1998; Zahedi Avval & Holmgren 2009). Both are re-reduced with NADPH as the donor of reducing equivalents. The relative contributions of glutaredoxin and thioredoxin in vivo are unknown.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [cytosol]
dNDP(3-) [cytosol]
NDP(3-) [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-111742
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
nucleoside 5'-diphosphate(3-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
water
2'-deoxyribonucleoside 5'-diphosphate(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-111742