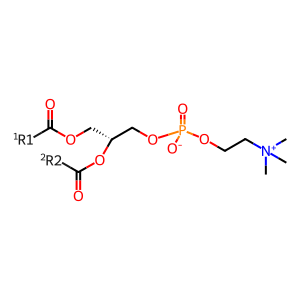
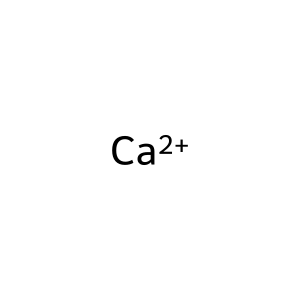Reaction: Phospho-cPLA2 translocates to membranes when intracellular calcium levels increase
- in pathway: phospho-PLA2 pathway
The 85kDa cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2 - PLA2G4A) is involved in cell signalling processes and inflammatory response and is regulated by phosphorylation and calcium concentrations. cPLA2 is phosphorylated at Ser727 and by a MAPK at Ser505. When phosphorylation is coupled with an influx of calcium ions, PLA2 becomes stimulated and translocates to the membrane where it releases arachidonic acid (AA) from membrane phospholipids. Calcium does not itself activate cPLA2. cPLA2 contains an N-terminal calcium-dependent phospholipid binding domain (CaLB) which shares homology with C2 domains (plays roles in signal transduction and membrane trafficking) and binds it to the membrane. Arachidonic acid is both a signalling molecule and the precursor for other signalling molecules termed eicosanoids (e.g., prostaglandins, leukotrienes and platelet-activating factor). A strict regulation of the activity of phospholipase enzyme is essential.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PC [endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
Ca2+ [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-111881
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
calcium(2+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-111881