Reaction: Addition of nucleotides leads to transcript elongation
- in pathway: RNA Polymerase II Transcription Elongation
High-resolution structures of free, catalytically active yeast Pol II and of an elongating form reveal that Pol II elongation complex includes features like:
- RNA-DNA hybrid, an unwound template ahead of 3'-OH terminus of growing transcript and an exit groove at the base of the CTD, possibly for dynamic interaction of processing and transcriptional factors.
- a cleft or channel created by Rpb1 and Rpb2 subunits to accommodate DNA template, extending to Mg2+ ion located deep in the enzyme core
-a 50 kDa "clamp" with open confirmation in free polymerase, allowing entry of DNA strands but closed in the processive elongation phase.
The clamp is composed of portions of Rpb1,Rpb2 and Rpb3 , five loops or "switches" that change from unfolded to well-folded structures stabilizing the elongation complex, and a long "bridging helix" that emanates from Rpb1 subunit, crossing near the Mg2+ ion. The bridging helix is thought to "bend" to push on the base pair at the 3'-end of RNA-DNA hybrid like a ratchet, translocating Pol II along the DNA (Cramer et al.,2001; Gnatt et al.,2001).In addition to its dynamic biochemical potential, Pol II possess a repertoire of functions to serve as a critical platform of recruiting and coordinating the actions of a host of additional enzyme and proteins involved in various pathways.
- RNA-DNA hybrid, an unwound template ahead of 3'-OH terminus of growing transcript and an exit groove at the base of the CTD, possibly for dynamic interaction of processing and transcriptional factors.
- a cleft or channel created by Rpb1 and Rpb2 subunits to accommodate DNA template, extending to Mg2+ ion located deep in the enzyme core
-a 50 kDa "clamp" with open confirmation in free polymerase, allowing entry of DNA strands but closed in the processive elongation phase.
The clamp is composed of portions of Rpb1,Rpb2 and Rpb3 , five loops or "switches" that change from unfolded to well-folded structures stabilizing the elongation complex, and a long "bridging helix" that emanates from Rpb1 subunit, crossing near the Mg2+ ion. The bridging helix is thought to "bend" to push on the base pair at the 3'-end of RNA-DNA hybrid like a ratchet, translocating Pol II along the DNA (Cramer et al.,2001; Gnatt et al.,2001).In addition to its dynamic biochemical potential, Pol II possess a repertoire of functions to serve as a critical platform of recruiting and coordinating the actions of a host of additional enzyme and proteins involved in various pathways.
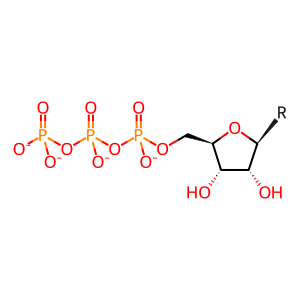
Reaction - small molecule participants:
NTP [nucleoplasm]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-112385
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
nucleoside 5'-triphoshate(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-112385