Reaction: ISGylation of viral protein NS1
- in pathway: ISG15 antiviral mechanism
Some viral proteins are also targeted for ISGylation. The well studied viral protein ISGylation is the modification of the influenza A viral protein NS1, which functions as an IFN antagonist during viral infection. Studies identified seven lysine residues in NS1 as potential ISGylation sites among which K41 (Zhao et al. 2010), K126 and K217 (Tang et al. 2010) were found to be critical. ISGylation at these sites disrupts NS1 association with importin-alpha, a protein required for the nuclear import of NS1.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PPi [cytosol]
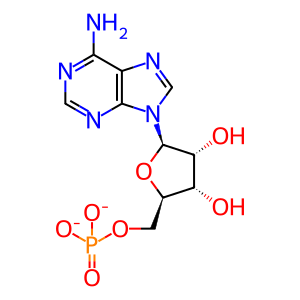
AMP [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1169395
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
ATP(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
diphosphate(3-)
adenosine 5'-monophosphate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1169395