Reaction: CA4:Zn2+ hydrates CO2 to HCO3-
- in pathway: Erythrocytes take up carbon dioxide and release oxygen
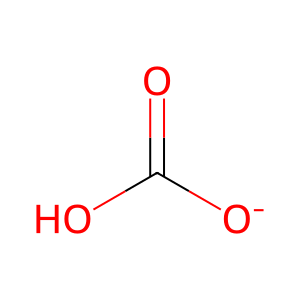
Carbonic anhydrase IV (CA4) anchored to extracellular face of the plasma membrane (Wistrand et al. 1999) hydrates carbon dioxide (CO2) to yield bicarbonate (HCO3-) and a proton (H+) (Zhu & Sly 1990, Okayuma et al. 1992, Baird et al. 1997, Innocenti et al. 2004). During the reaction a hydroxyl group bound by the zinc ion (Zn2+) of CA4 attacks the CO2 molecule to directly form HCO3- (reviewed in Lindskog 1997). The HCO3- is displaced by water, which is then deprotonated by a histidine residue to recreate the Zn2+:hydroxyl group. Depending on the concentrations of reactants the reaction is reversible.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [extracellular region]
HCO3- [extracellular region]
H2O [extracellular region]
CO2 [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1237047
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
carbon dioxide
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
hydrogencarbonate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1237047