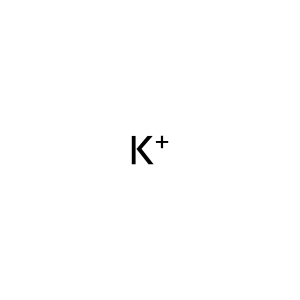Reaction: Activation of Ca2+ activated Potassium channels with large conductance
- in pathway: Ca2+ activated K+ channels
Increase in intracellular concentration of Ca2+ ions and membrane depolarization cooperatively activates BKca, which exhibit large unitary conductance. Ca2+ activated potassium channels. Activation leads to K+ efflux which changes the membrane potential, which leads to inactivation voltage activated Ca2+ channels. BKca are involved in regulation of smooth muscle tone, microbial killing in leukocytes and modulation of neurotransmitter release.
Activation of BKca channel with increase in intracellular concentration of Ca2+ leads to efflux of K+ into the extracellular space, which contributes to hyperpolarization of the membrane potential.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
K+ [extracellular region]
K+ [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1296037
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
potassium(1+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
potassium(1+)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1296037