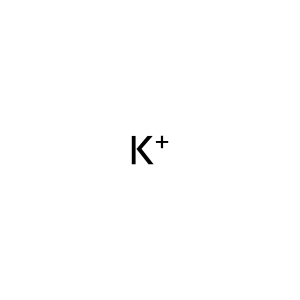Reaction: Activation of ATP sensitive Potassium channels in muscle cells
- in pathway: ATP sensitive Potassium channels
In muscle cells such as cardiac, skeletal, vascular and nonvascular smooth muscle, ATP sensitive K+ channels assemble as octamers of four Kir 6.x subunits and four low-affinity sulfonyl urea receptor 2 subunits (SUR2). The human gene encoding SUR2 gives rise to two splice variants, SUR2A and SUR2B. These channels are blocked by excess intracellular levels of ATP. When the ATP is low, ATP dissociates and the channel opens to allow K+ efflux (Krenz et al. 2002).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
K+ [extracellular region]
K+ [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1369017
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
potassium(1+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
potassium(1+)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1369017