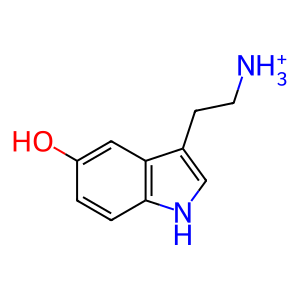
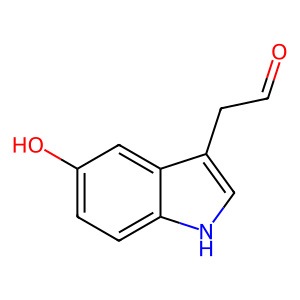
Reaction: MAOA:FAD oxidatively deaminates of 5HT
Amine oxidase (flavin-containing) A (MAOA) catalyses the oxidative deamination of biogenic and dietary amines, the regulation of which is critical for mental state homeostasis. MAOA, located on the mitochondrial outer membrane and requiring FAD as cofactor (Weyler 1989), preferentially oxidises biogenic amines such as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5HT), dopamine, noradrenaline and adrenaline (latter three not shown here). 5HT is deaminated to 5-hydroxyindolacetaldehyde (5HIALD).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
5HIALD [cytosol]
NH4+ [cytosol]
H2O2 [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
5HT [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
5HIALD [cytosol]
NH4+ [cytosol]
H2O2 [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
5HT [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-141186
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
serotonin(1+)
dioxygen
water
serotonin(1+)
dioxygen
Reaction output - small molecules:
(5-hydroxyindol-3-yl)acetaldehyde
ammonium
hydrogen peroxide
(5-hydroxyindol-3-yl)acetaldehyde
ammonium
hydrogen peroxide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-141186