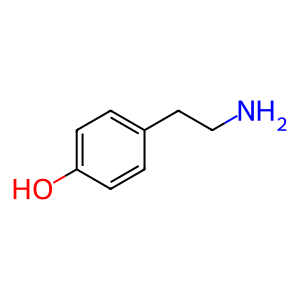
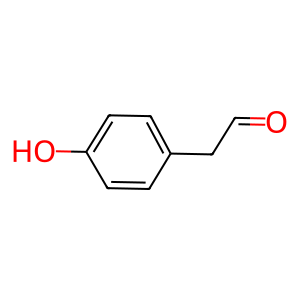
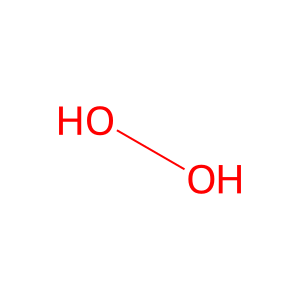
Reaction: MAOB:FAD oxidatively deaminates TYR
Monoamine oxidases (MAOA and B), present in the outer mitochondrial membrane, catalyse the oxidation of biogenic amines, releasing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). H2O2 produced during the oxidative deamination of these amines appears to be involved in the progress of neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson disease, presumably via oxidative damage to the mitochondrial membrane. MAOB (also MAOA but not show here), with FAD as cofactor, can deaminate tyramine (TYR), a naturally-occuring monoamine that can act as a catecholamine releasing agent (Pearce & Roth 1985).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
HPHAC [cytosol]
NH3 [cytosol]
H2O2 [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
TYR [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-141202
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
tyramine
dioxygen
Reaction output - small molecules:
(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetaldehyde
ammonia
hydrogen peroxide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-141202