Reaction: ABCG4 may mediate cholesterol efflux
- in pathway: ABC transporters in lipid homeostasis
Human ABCG4 shows sequence homology to the Drosophila white gene, the product of which must dimerise to become functionally active. ABCG4 is closely related to ABCG1 with 74% identity and is thus thought to play a role in the efflux of excess cholesterol (Engel et al. 2001). Northern Blot analysis shows that ABCG4 is expressed specifically in brain and the eye (Oldfield et al. 2002).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
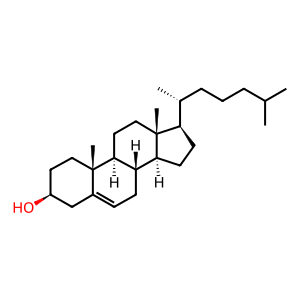
CHOL [extracellular region]
Pi [cytosol]
ADP [cytosol]
CHOL [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1454928
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
cholesterol
water
ATP(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
cholesterol
hydrogenphosphate
ADP(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1454928