Reaction: ABCA4 mediates atRAL transport
- in pathway: ABC-family proteins mediated transport
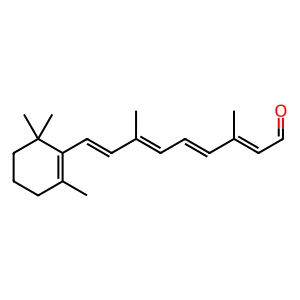
Rhodopsin (RHO) is localised to both the disc membrane and the plasma membrane of rod outer segments (ROS). All-trans-retinal (atRAL) released from rhodopsin during the bleaching process, needs to translocate to the cytosol for reduction to all-trans-retinol (atROL) via all-trans-retinol dehydrogenases. Although atRAL can diffuse through membranes unaided, there exists an ABC transporter on disc membranes which may facilitate the transport of excess atRAL. Retinal-specific ATP-binding cassette transporter (ABCA4, ABCR) is the only ABC transporter which mediates the transport of retinoids (Biswas & Biswas 2000). Studies using bovine ABCA4 demonstrates atRAL transport (Sun et al. 1999). Human ABCR was found to be identical to the ABC transporter linked to Stargardt's disease type 1 (STGD1, MIM:248200), a cause of macular degeneration in childhood (Nasonkin et al. 1998).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Pi [cytosol]
ADP [cytosol]
atRAL [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
atRAL [photoreceptor disc membrane]
Pi [cytosol]
ADP [cytosol]
atRAL [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
atRAL [photoreceptor disc membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1467466
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
ATP(4-)
all-trans-retinal
water
ATP(4-)
all-trans-retinal
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydrogenphosphate
ADP(3-)
all-trans-retinal
hydrogenphosphate
ADP(3-)
all-trans-retinal
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1467466