Reaction: Carbonic anhydrase dehydrates bicarbonate (plasma membrane)
- in pathway: Reversible hydration of carbon dioxide
Carbonic anhydrase IV (CA4, Zhu and Sly 1990, Okuyama et al. 1992, Baird et al. 1997, Innocenti et al. 2004), carbonic anhydrase IX (CA9, Wingo et al. 2001, Hilvo et al. 2008), carbonic anhydrase XII (CA12, Ulmasov et al. 2000, Pastorekova et al. 2008), and carbonic anhydrase XIV (CA14, Ozensoy et al. 2005, Temperini et al. 2008) are membrane-bound enzymes that dehydrate bicarbonate to yield water and carbon dioxide. Depending on the concentrations of reactants the reaction is reversible.
CA4 has high catalytic activity. CA9, CA12, and CA14 have moderate activity. CA4 is anchored to the extracellular face of the plasma membrane by glycosylphosphatidylinositol. CA9, CA12, and CA14 are single-pass transmembrane proteins. CA4 is found on the extracellular face of capillaries in kidney, lung, and muscle where it maintains the gradient of carbon dioxide between tissue and blood. CA9 and CA12 are found on basolateral membranes of epithelia. CA9 is inducible by Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF1alpha) and acidifies the extracellular environment of tumors. In rodents CA15 is membrane anchored and has low activity; in primates CA15 is a pseudogene.
CA4 has high catalytic activity. CA9, CA12, and CA14 have moderate activity. CA4 is anchored to the extracellular face of the plasma membrane by glycosylphosphatidylinositol. CA9, CA12, and CA14 are single-pass transmembrane proteins. CA4 is found on the extracellular face of capillaries in kidney, lung, and muscle where it maintains the gradient of carbon dioxide between tissue and blood. CA9 and CA12 are found on basolateral membranes of epithelia. CA9 is inducible by Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF1alpha) and acidifies the extracellular environment of tumors. In rodents CA15 is membrane anchored and has low activity; in primates CA15 is a pseudogene.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [extracellular region]
CO2 [extracellular region]
H+ [extracellular region]
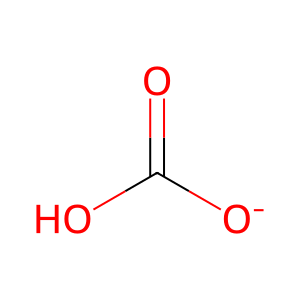
HCO3- [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1475017
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydron
hydrogencarbonate
Reaction output - small molecules:
water
carbon dioxide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1475017