Reaction: Carbonic anhydrase dehydrates bicarbonate (cytosol)
- in pathway: Reversible hydration of carbon dioxide
Carbonic anhydrase I (CA1, Khalifah 1971, Simonsson et al. 1982, Ren and Lindskog 1992), carbonic anyhydrase II (CA2, Tibell et al. 1984, Jones and Shaw 1983, Pesando 1975, Ghannam et al. 1986), carbonic anhydrase III (CA3, Carter et al. 1979, Tu et al. 1990, Tu et al. 1994, Tu et al. 1998, Silverman et al. 1993), carbonic anhydrase VII (CA7, Bootorabi et al. 2010, Gitto et al. 2010) dehydrate cytosolic bicarbonate to yield water and carbon dioxide (reviewed in Lindskog 1997). Depending on the concentrations of reactants the reaction is reversible.
CA2 and CA7 have high catalytic activity, CA1 has low activity (10% of the activity of CA2), and CA3 has very low activity (1% of the activity of CA2). CA1 and CA2 are found in erythrocytes. CA2 is also found in kidney, lung, and white muscle where it facilitates diffusion of carbon dioxide. CA3 is found in red muscle where it participates in resistance against oxidative stress.
CA2 and CA7 have high catalytic activity, CA1 has low activity (10% of the activity of CA2), and CA3 has very low activity (1% of the activity of CA2). CA1 and CA2 are found in erythrocytes. CA2 is also found in kidney, lung, and white muscle where it facilitates diffusion of carbon dioxide. CA3 is found in red muscle where it participates in resistance against oxidative stress.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [cytosol]
CO2 [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
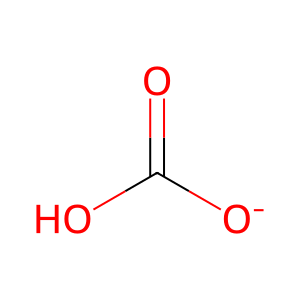
HCO3- [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1475022
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydron
hydrogencarbonate
Reaction output - small molecules:
water
carbon dioxide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1475022