Reaction: Carbonic anhydrase hydrates carbon dioxide (mitochondria)
- in pathway: Reversible hydration of carbon dioxide
Carbonic anhydrase VA (CA5A, Nagao et al. 1993, Franchi et al. 2003, Nishimori et al. 2007) and carbonic anhydrase VB (CA5B, Fujikawa-Adachi et al. 1999, Nishimori et al. 2005, Nishimori et al. 2007) hydrate carbon dioxide in mitochondria to yield bicarbonate and a proton. Carbonic anhydrase deprotonates water to yield a zinc-hydroxyl group and a proton which is transferred to external buffer molecules via histidine or glutamate residues in carbonic anhydrase. The hydroxyl group reacts with carbon dioxide in the active site to yield bicarbonate. A water molecule displaces the bicarbonate and the reaction cycle begins again (reviewed in Lindskog 1997). Depending on the concentrations of reactants the reaction is reversible.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
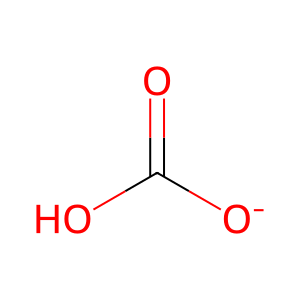
HCO3- [mitochondrial matrix]
H+ [mitochondrial matrix]
H2O [mitochondrial matrix]
CO2 [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1475032
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
carbon dioxide
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydrogencarbonate
hydron
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1475032