Reaction: CA1:Zn2+,CA2:Zn2+ dehydrate HCO3- to CO2
- in pathway: Erythrocytes take up oxygen and release carbon dioxide
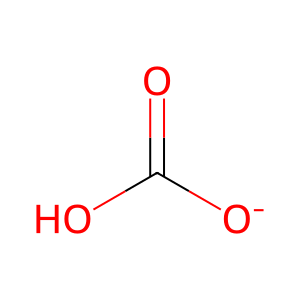
Carbonic anhydrase I (CA1, Khalifah 1971, Pesando 1975, Simonsson et al. 1982, Ren & Lindskog 1992) and carbonic anhydrase II (CA2, Tibell et al. 1984, Jones & Shaw 1983, Ghannam et al. 1986) hydrate carbon dioxide (CO2) to yield bicarbonate (HCO3-) and a proton (H+). During the reaction a hydroxyl group bound by the zinc ion (Zn2+) attacks the CO2 molecule in the active site to directly form HCO3- (reviewed in Lindskog 1997). The HCO3- is displaced by water, which is then deprotonated by a histidine residue to recreate the Zn2+:hydroxyl group. Depending on the concentrations of reactants the reaction is reversible.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [cytosol]
CO2 [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
HCO3- [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1475436
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydron
hydrogencarbonate
Reaction output - small molecules:
water
carbon dioxide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1475436