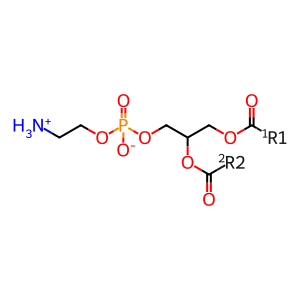
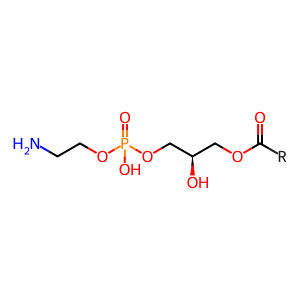
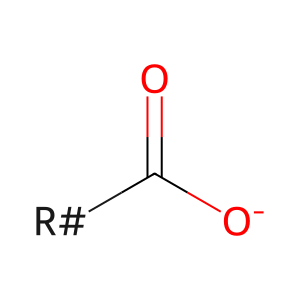
Reaction: PE is hydrolyzed to 1-acyl LPE by PLA2[2]
- in pathway: Acyl chain remodelling of PE
At the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane, phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) is hydrolyzed, and has one of its acyl chains cleaved off, by phospholipase A2 to form 1-acyl lysophosphatidylethanolamine (LPE). The phospholipases are either cytosolic phospholipase A2 alpha/beta/delta/epsilon/zeta (PLA2G(4A/B/D/E/F) (Ghosh et al. 2006, Yamashita et al. 2009, Yamashita et al. 1999, Ghomashchi et al. 2010), 85 kDa calcium-independent phospholipase A2 (PLA2G6) (Larsson et al. 1998, Ma et al. 1999, Larsson Forsell et al. 1999), group XVI phospholipase A2 (PLA2G16) (Duncan et al. 2008), or Phospholipase B-like 1 (PLBD1) (Xu et al. 2009). PLBD1 acts as a phospholipase A2 but in addition has the propensity to hydrolyze the lysophospholipid formed in its initial reaction.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
1-acyl LPE [endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
LCFA(-) [endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
H2O [cytosol]
PE [endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1482884
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
phosphatidylethanolamine zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
1-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine
long-chain fatty acid anion
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1482884