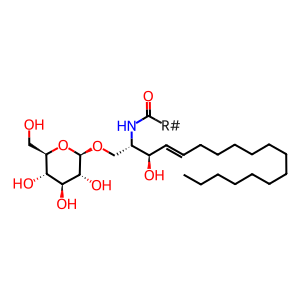
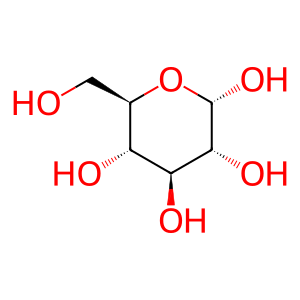
Reaction: GBA1:SAPC hydrolyzes GlcCer
- in pathway: Glycosphingolipid catabolism
Human lysosomal glucosylceramidase (GBA1) hydrolyzes the glucosidic bond of glucocerebrosides (GlcCer) to form ceramide (Dinur et al. 1986). GBA1 requires a low-weight, non-enzymatic protein (one of the sphingolipids activator proteins) called Saposin-C (SAP-C) which acts with GBA1 to form an activated complex (Salvioli et al. 2000; Abdul-Hammed et al., 2017). Defects in GBA1 are the cause of Gaucher disease (GD) (MIM:230800), the most common glycolipid storage disorder, characterized by storage of glucocerebroside in the liver, spleen, and marrow (Beutler & Gelbart 1996).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Glc [lysosomal lumen]
CERA [lysosomal lumen]
H2O [lysosomal lumen]
GlcCer [lysosomal lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1605591
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
GlcCer
Reaction output - small molecules:
alpha-D-glucose
N-acylsphingoid
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1605591