Reaction: GLB1 hydrolyses mobilized GM1 to mobilized GM2
- in pathway: Glycosphingolipid catabolism
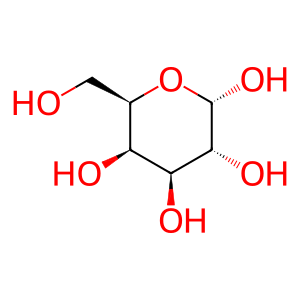
The prototypical ganglioside GM1 is hydrolyzed to the GM2 ganglioside by beta-galactosidase (GLB1), cleaving off the terminal galactose (Asp et al. 1969). Either Saposin B (PSAP(195-273)) or ganglioside GM2 activator (GM2A, GM2AP) acts as a cofactor (Wilkening et al., 2000). Defects in GLB1 cause the lysosomal storage diseases GM1-gangliosidosis (Yoshida et al. 1991; reviewed in Brunetti-Pierri & Scaglia, 2008) and Morquio syndrome B (Oshima et al. 1991). GLB1L, GLB1L2, and GLB1L3 are gene products with nearly identical protein sequences to GLB1 and may be able to perform the same function.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Gal [lysosomal lumen]
H2O [lysosomal lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1605624
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
alpha-D-galactose
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1605624