Reaction: NEU1,4 hydrolyze PSAP(195-273):GM3:PE
- in pathway: Glycosphingolipid catabolism
Ganglioside GM3, mobilized by Saposin B (PSAP(195-273)), is hydrolyzed by sialidases to lactosylceramide (LacCer). Sialidases (NEU, neuraminidases) hydrolyze sialic acids (N-acetylneuramic acid, Neu5Ac, NANA) to produce asialo compounds, a step in the degradation process of glycoproteins and gangliosides. NEU1 and NEU4 hydrolyse NANA in the lysosomal lumen. NEU1 is active in a multienzyme complex comprising cathepsin A protective protein (CTSA) and beta-galactosidase (Bonten et al. 1996, Rudenko et al. 1995). Defects in NEU1 cause Sialidosis (MIM:256550) (Bonten et al. 1996). CTSA appears to exert a protective function necessary for the stability and activity of these enzymes (Galjart et al. 1988). Defects in CTSA are the cause of galactosialidosis (GSL, MIM:256540) (Zhou et al. 1991). NEU4 is also a lysosomal sialidase which, unlike NEU1, does not require association with other proteins for enzymatic activity. Isoform 2 seems to be the lysosomal sialidase (Seyrantepe et al. 2004). Researchers observed elevated GM3 in prosaposin deficiency (PSAPD, MIM: 611721) cases, a rare disease with low levels of all saposins. The essential cofactor missing appears to be Saposin B (PSAP(195-273)) (Schmidt et al., 1992; Bradova et al., 1993).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
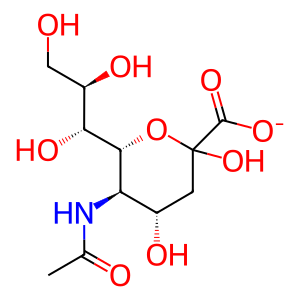
Neu5Ac [lysosomal lumen]
H2O [lysosomal lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1605724
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
N-acetylneuraminate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1605724