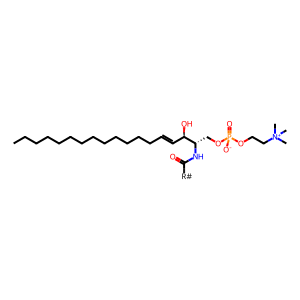
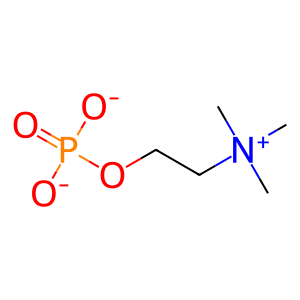
Reaction: SMPD1 hydrolyzes SPHM
- in pathway: Glycosphingolipid catabolism
Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase (SMPD1), also called acid sphingomyelinase (ASM), is a lysosomal phosphodiesterase that hydrolyses sphingomyelin to ceramide and phosphocholine (Schuchman et al. 1991, Schuchman et al. 1992). Defects in SMPD1 are the cause of two types of Niemann-Pick disease. Type A (NPDA, Niemann-Pick disease classical infantile form) (MIM:257200) (Ferlinz et al. 1991) and type B (NPDB, Niemann-Pick disease visceral form) (MIM:607616) (Rodriguez-Pascau et al. 2009).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [lysosomal lumen]
ChoP [lysosomal lumen]
CERA [lysosomal lumen]
H2O [lysosomal lumen]
SPHM [lysosomal lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1605797
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
sphingomyelin d18:1
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
choline phosphate(1-)
N-acylsphingoid
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1605797