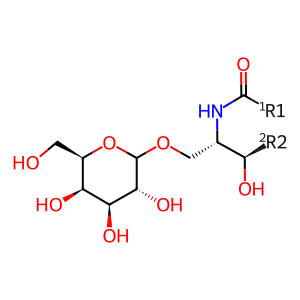
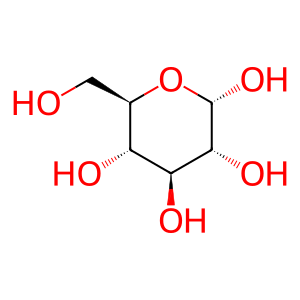
Reaction: GALC hydrolyzes GalCer
- in pathway: Glycosphingolipid catabolism
Galactocerebrosidase (GALC) hydrolyses the galactosyl moiety from galactocerebroside (also called galactosylceramide, GalCer) to form ceramide (Sakai et al. 1994). Saposin A stimulates the reaction (Sap A, PSAP(60-142)) (Morimoto et al., 1989). Defects in GALC are the cause of leukodystrophy globoid cell (GLD) (MIM:245200), also called Krabbe disease (Chen et al., 1993; Chen & Wenger, 1993; Wenger et al., 1997). Defects in Sap A cause an atypical form of Krabbe disease (KRBSAPA, MIM:611722) (Spiegel et a., 2005).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Glc [lysosomal lumen]
CERA [lysosomal lumen]
H2O [lysosomal lumen]
GalCer [lysosomal lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1606564
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
galactosylceramide
Reaction output - small molecules:
alpha-D-glucose
N-acylsphingoid
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1606564