Reaction: ARSB hydrolyses DS
- in pathway: CS/DS degradation
Arylsulfatase B (ARSB) hydrolyses sulfate from N-acetylgalactosamine 4-sulfate units within dermatan sulfate (DS; Gorham & Cantz 1978). The conversion to 3-oxoalanine (formylglycine, FGly) of a cysteine residue in eukaryotes, is critical for catalytic activity, based on similarity to the prototypical arylsulfatase ARSA (Chruszcz et al. 2003, Lukatela et al. 1998). Defects in ARSB are the cause of mucopolysaccharidosis type VI (MPSVI) (MIM:253200, also called Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome (Wicker et al. 1991). ARSB activity is defective in multiple sulfatase deficiency (MSD) (MIM:272200) (Schmidt et al. 1995).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
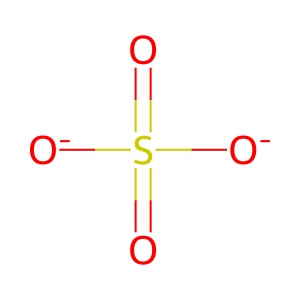
SO4(2-) [lysosomal lumen]
ChEBI:63517 chain [lysosomal lumen]
H2O [lysosomal lumen]
ChEBI:63519 chain [lysosomal lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1606789
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
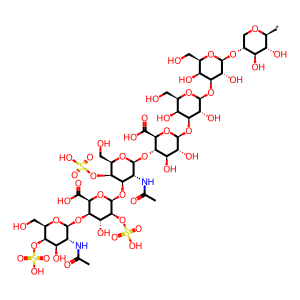
beta-D-GalNAc4S-(1->4)-beta-D-IdoA2S-(1->3)-beta-D-GalNAc4S-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcA-(1->3)-beta-D-Gal-(1->3)-beta-D-Gal-(1->4)-beta-D-Xyl-yl group
Reaction output - small molecules:
sulfate
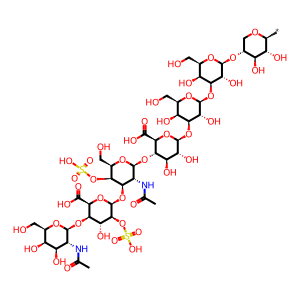
beta-D-GalNAc-(1->4)-beta-D-IdoA2S-(1->3)-beta-D-GalNAc4S-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcA-(1->3)-beta-D-Gal-(1->3)-beta-D-Gal-(1->4)-beta-D-Xyl-yl group
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1606789