Reaction: ARSC hydrolyzes steroid sulfates
- in pathway: Metabolism of steroid hormones
Steryl sulfatase (formerly arylsulfatase C, ARSC) hydrolyses sulfate from steroid sulfates (Noel et al. 1983, Vaccaro et al. 1987, Suzuki et al. 1992). It is located on the ER membrane (Stein et al. 1989) and functions as a homodimer, using calcium as a cofactor. Defects in STS are the cause of ichthyosis X-linked (IXL) (MIM:308100), a keratinisation disorder (Basler et al. 1992, Alperin & Shapiro 1997).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
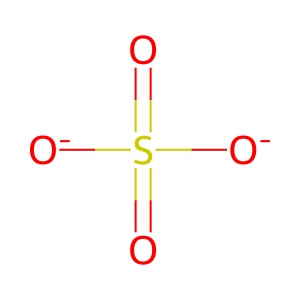
SO4(2-) [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
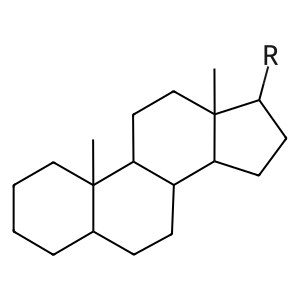
steroid [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
H2O [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
steroid sulfate [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1606839
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
steroid sulfate oxoanion
Reaction output - small molecules:
sulfate
steroid
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1606839