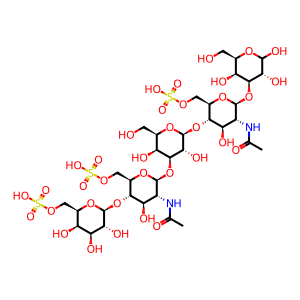
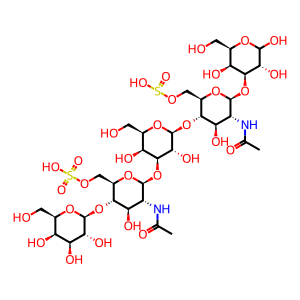
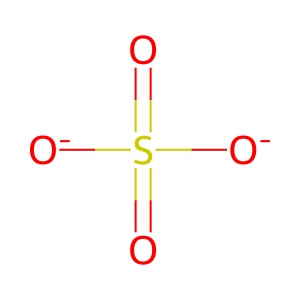
Reaction: GALNS oligomer hydrolyses sulfate from Gal6S in keratan sulfate
- in pathway: Keratan sulfate degradation
N-acetylgalactosamine 6-sulfate sulfatase (GALNS) hydrolyses sulfate from galactose 6-sulfate units of keratan sulfate (KS, shown here) and sulfate from N-acetyl-D-galactosamine 6-sulfate units of chondroitin sulfate (CS, not shown) (Lim & Horwitz 1981, Masue et al. 1991). The conversion to 3-oxoalanine (C-formylglycine, FGly) of a cysteine residue in eukaryotes, is critical for catalytic activity, based on similarity to the prototypical arylsulfatase ARSA (Chruszcz et al. 2003, Lukatela et al. 1998). Defects in GALNS cause mucopolysaccharidosis type IVA (MPSIVA, MIM:253000), also called Morquio A syndrome, a lysosomal storage disease characterized by intracellular accumulation of KS and CS (Fukuda et al. 1992).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Gal-GlcNAc(S)-Gal-GlcNAc(S)-Gal [lysosomal lumen]
SO4(2-) [lysosomal lumen]
Gal(S)-GlcNAc(S)-Gal-GlcNAc(S)-Gal [lysosomal lumen]
H2O [lysosomal lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1630304
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
beta-D-Galp6S-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcpNAc6S-(1->3)-beta-D-Galp-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcpNAc6S-(1->3)-D-Galp
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
beta-D-Galp-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcpNAc6S-(1->3)-beta-D-Galp-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcpNAc6S-(1->3)-D-Galp
sulfate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1630304