Reaction: Transfer of electrons through the succinate dehydrogenase complex
- in pathway: Respiratory electron transport
This event is deduced on the basis of bovine experimental data.
Complex II (succinate dehydrogenase) transfers electrons from the TCA cycle to ubiquinone. The 6th step in the TCA cycle is where succinate is dehydrogenated to fumarate with subsequent reduction of FAD to FADH2. FADH2 provides the electrons for the transport chain. Succinate dehydrogenase belongs to subclass 1 of the SQR family (succinate:quinone reductase) (classified by Hagerhall, C and Hederstedt, L [1996]).
It consists of 4 subunits (referred to as A, B, C and D), all nuclear-encoded and is located on the matrix side of the inner mitochondrial membrane. Subunits A and B are hydrophilic whereas subunits C and D are integral proteins of the inner membrane. SQRs usually contain 3 Fe-S clusters bound by the B subunit. Succinate dehydrogenase contains one [2Fe-2S] cluster, one [4Fe-4S] cluster and one [3Fe-4S] cluster. Additionally, the A subunit has a covalently-bound FAD group. Reduced complex II has this FAD converted to FADH2. The electrons from complex II are transferred to ubiquinone (also called Q, Coenzyme Q or CoQ), a small mobile carrier of electrons located within the inner membrane. Ubiquinone is reduced to ubiquinol during this process.
The mitochondrial heat shock protein 75 kDa (TRAP1) inhibits Complex II of the respiratory chain which elicits respiratory downregulation, leading to a pseudohypoxic state. This state is caused by succinate-dependent HIF1-alpha stabilisation which, in turn, can promote tumorigenesis (Sciacovelli et al. 2013, Yoshida et al. 2013, Guzzo et al. 2014).
Complex II (succinate dehydrogenase) transfers electrons from the TCA cycle to ubiquinone. The 6th step in the TCA cycle is where succinate is dehydrogenated to fumarate with subsequent reduction of FAD to FADH2. FADH2 provides the electrons for the transport chain. Succinate dehydrogenase belongs to subclass 1 of the SQR family (succinate:quinone reductase) (classified by Hagerhall, C and Hederstedt, L [1996]).
It consists of 4 subunits (referred to as A, B, C and D), all nuclear-encoded and is located on the matrix side of the inner mitochondrial membrane. Subunits A and B are hydrophilic whereas subunits C and D are integral proteins of the inner membrane. SQRs usually contain 3 Fe-S clusters bound by the B subunit. Succinate dehydrogenase contains one [2Fe-2S] cluster, one [4Fe-4S] cluster and one [3Fe-4S] cluster. Additionally, the A subunit has a covalently-bound FAD group. Reduced complex II has this FAD converted to FADH2. The electrons from complex II are transferred to ubiquinone (also called Q, Coenzyme Q or CoQ), a small mobile carrier of electrons located within the inner membrane. Ubiquinone is reduced to ubiquinol during this process.
The mitochondrial heat shock protein 75 kDa (TRAP1) inhibits Complex II of the respiratory chain which elicits respiratory downregulation, leading to a pseudohypoxic state. This state is caused by succinate-dependent HIF1-alpha stabilisation which, in turn, can promote tumorigenesis (Sciacovelli et al. 2013, Yoshida et al. 2013, Guzzo et al. 2014).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
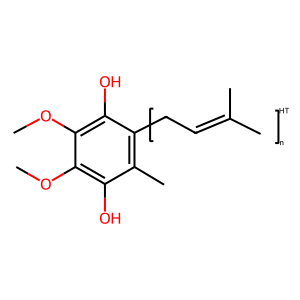
QH2 [mitochondrial inner membrane]
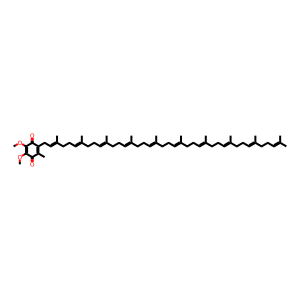
CoQ [mitochondrial inner membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-163213
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
coenzyme Q10
Reaction output - small molecules:
ubiquinol
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-163213