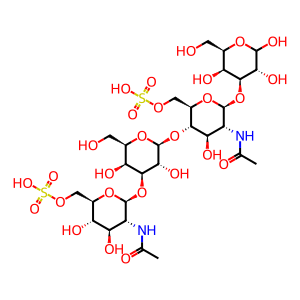
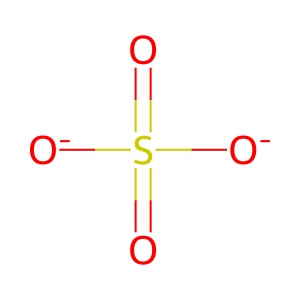
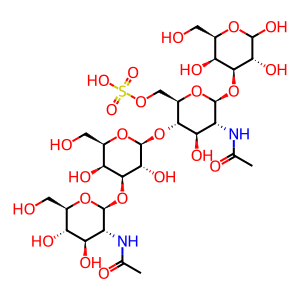
Reaction: N-acetylglucosamine 6-sulfatase (GNS) hydrolyses 6-sulfate groups of the N-acetyl-D-glucosamine 6-sulfate units of keratan sulfate
- in pathway: Keratan sulfate degradation
N-acetylglucosamine 6-sulfatase (GNS) is a lysosomal enzyme which degrades glycosaminoglycans such as heparan sulfate and keratan sulfate. GNS shows strong sequence similarity to other sulphatases such as the family of arylsulfatases and the conversion to 3-oxo-alanine (formylglycine, FGly) of a cysteine residue is critical for catalytic activity, based on this similarity (Robertson et al. 1992, Robertson et al. 1988). Defects in GNS are the cause of mucopolysaccharidosis type IIID (MPSIIID, MIM:252940), also called Sanfilippo D syndrome (Valstar et al. 2010).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
SO4(2-) [lysosomal lumen]
GlcNAc-Gal-GlcNAc(S)-Gal [lysosomal lumen]
H2O [lysosomal lumen]
GlcNAc(S)-Gal-GlcNAc(S)-Gal [lysosomal lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1638032
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
beta-D-GlcpNAc6S-(1->3)-beta-D-Galp-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcpNAc6S-(1->3)-D-Galp
Reaction output - small molecules:
sulfate
beta-D-GlcpNAc-(1->3)-beta-D-Galp-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcpNAc6S-(1->3)-D-Galp
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1638032