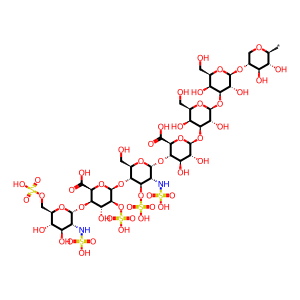
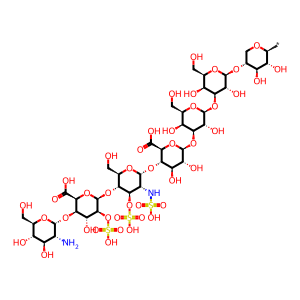
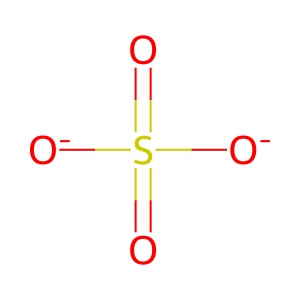
Reaction: SGSH hydrolyses Heparan sulfate chain(2)
- in pathway: HS-GAG degradation
N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase (SGSH) hydrolyses the sulfate group from the terminal N-sulphoglucosamine residue of heparan sulfate (Scott et al. 1995). Defects in SGSH cause mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIA (MPSIIIA, MIM:252900), also called Sanfilippo syndrome A (Weber et al. 1997).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Heparan sulfate chain(3) [lysosomal lumen]
SO4(2-) [lysosomal lumen]
H2O [lysosomal lumen]
Heparan sulfate chain(2) [lysosomal lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1678708
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
alpha-D-GlcNS6S-(1->4)-beta-D-IdoA2S-(1->4)-alpha-D-GlcNS3S-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcA-(1->3)-beta-D-Gal-(1->3)-beta-D-Gal-(1->4)-beta-D-Xyl-yl group
Reaction output - small molecules:
alpha-D-GlcN-(1->4)-beta-D-IdoA2S-(1->4)-alpha-D-GlcNS3S-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcA-(1->3)-beta-D-Gal-(1->3)-beta-D-Gal-(1->4)-beta-D-Xyl-yl group
sulfate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1678708