Reaction: Elongation, Polyadenylation and Termination
- in pathway: Viral Messenger RNA Synthesis
Catalyzed by the RNA polymerase activity of the viral PB1 subunit, an mRNA complementary to the bound vRNA is synthesized (Plotch, 1977). PA and PB2 move down the growing mRNA in complex with PB1, with PB2 possibly dissociating from the cap (Braam, 1983). However, the 5’ end of the vRNA may remain bound during elongation as the template is threaded through in a 3’ to 5’ direction until a polyadenylation signal is encountered (Poon, 1998; Zheng, 1999).
A poly-uridine sequence motif, consisting in most cases of 5-7 U residues, abuts the "panhandle" duplex structure in the vRNA; this sequence is approximately 16 nucleotides from the 5' end of this RNA duplex structure within the vRNA promoter. Encountering this signal, the viral RNA polymerase stutters, leading to the synthesis of a poly-A tail on the viral mRNA (Robertson, 1981; Luo, 1991; Li,1994; Poon, 1998; Zheng et al. 1999).
A poly-uridine sequence motif, consisting in most cases of 5-7 U residues, abuts the "panhandle" duplex structure in the vRNA; this sequence is approximately 16 nucleotides from the 5' end of this RNA duplex structure within the vRNA promoter. Encountering this signal, the viral RNA polymerase stutters, leading to the synthesis of a poly-A tail on the viral mRNA (Robertson, 1981; Luo, 1991; Li,1994; Poon, 1998; Zheng et al. 1999).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
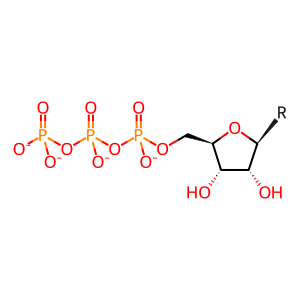
NTP [nucleoplasm]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-168301
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
nucleoside 5'-triphoshate(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-168301