Reaction: MAT1A multimers transfer Ado from ATP to L-Met
- in pathway: Sulfur amino acid metabolism
S-adenosylmethionine (AdoMet, SAM) is an essential metabolite in all cells. AdoMet is a precursor in the synthesis of polyamines. Methionine adenosyltransferases (MAT) catalyse the only known AdoMet biosynthetic reaction from methionine (L-Met) and ATP. In mammalian tissues, three different forms of MAT (MAT I, MAT III and MAT II) have been identified that are the product of two different genes (MAT1A and MAT2A). MAT1A binds 1 K+ and 2 Mg2+ (or Co2+, not shown here) in tetrameric or dimeric form (Corrales et al. 2002, Mato et al. 1997).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PPi [cytosol]
Pi [cytosol]
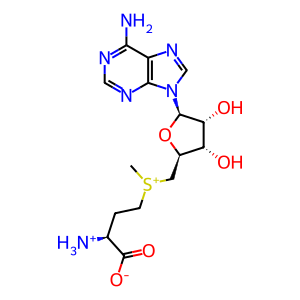
AdoMet [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
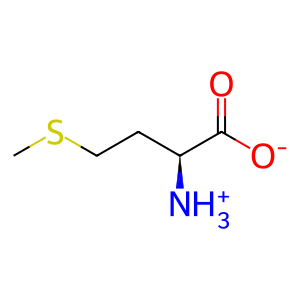
L-Met [cytosol]
PPi [cytosol]
Pi [cytosol]
AdoMet [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
L-Met [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-174391
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
ATP(4-)
L-methionine zwitterion
water
ATP(4-)
L-methionine zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
diphosphate(3-)
hydrogenphosphate
S-adenosyl-L-methionine zwitterion
diphosphate(3-)
hydrogenphosphate
S-adenosyl-L-methionine zwitterion
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-174391