Reaction: PAPSS1,2 transfer SO4(2-) group to ATP to form APS
- in pathway: Transport and synthesis of PAPS
In the first step of PAPS biosynthesis, ATP and sulfate react to form adenylyl sulfate (APS) and pyrophosphate (PPi), catalyzed by the ATP sulfurylase domains of the bifunctional enzymes PAPS synthases 1 and 2 (PAPSS1 and 2). PAPSS2 is essential for the sulfation of glycosaminoglycan chains in proteoglycans, a necessary post translational modification. Defective PAPSS2 results in undersulfation of the glycosaminoglycan chains in proteoglycans which causes spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia Pakistani type (SEMD PA; MIM:612847), a bone disease characterized by epiphyseal dysplasia with mild metaphyseal abnormalities. Mutations resulting in SEMD PA include S438*, T48R and R329* (Ahmad et al. 1998, ul Haque et al. 1998, Noordam et al. 2009).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PPi [cytosol]
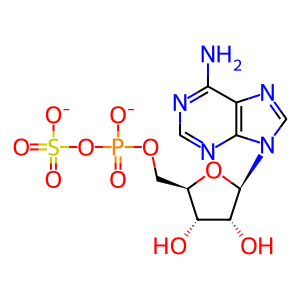
APS [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
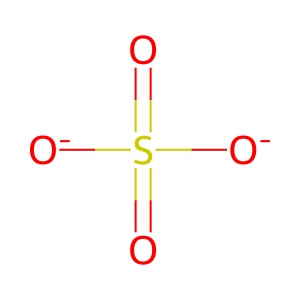
SO4(2-) [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-174392
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydron
ATP(4-)
sulfate
Reaction output - small molecules:
diphosphate(3-)
5'-adenylyl sulfate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-174392