Reaction: GST dimers conjugate GSH with cytosolic substrates
- in pathway: Glutathione conjugation
The glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) catalyze the nucleophilic attack by reduced glutathione (GSH) on nonpolar compounds that contain an electrophilic carbon, nitrogen, or sulphur atom. Their substrates include halogenonitrobenzenes, arene oxides, quinones, and alpha, beta-unsaturated carbonyls. Three major families of proteins are widely distributed in nature. Two of these, the cytosolic and mitochondrial GST, comprise soluble enzymes that are only distantly related whilst the third family comprises microsomal GST, referred to as membrane-associated proteins in eicosanoid and glutathione (MAPEG) metabolism.
At least 16 cytosolic GST subunits exist in human which are all in a dimeric form. Based on amino acid sequence similarities, seven classes of cytosolic GST are recognized in mammalian species; Alpha, Mu, Pi, Sigma, Theta, Omega, and Zeta (2–5). As well as being homodimers, the Alpha and Mu classes are also able to form heterodimers so a large number of isozymes are possible from all cytosolic GST subunits (Sinning et al. 1993, LeTrong et al. 2002, Ahmad et al. 1993, Pastore et al. 1998, Tars et al. 2010, Bruns et al. 1999, Balogh et al. 2010, Morel et al. 2002, Li et al. 2005, Patskovsky et al. 2006, Raghunathan et al. 1994, Patskovsky et al. 1999, Comstock et al. 1994, Board et al. 2000, Zhou et al. 2011, Zhou et al. 2012, Sun et al. 2011, Tars et al. 2006, Rossjohn et al. 1998, Polekhina et al. 2001, Inoue et al. 2003). Typical electrophilic substrates are chosen as examples for which the majority of the cytosolic GST isozymes act on.
At least 16 cytosolic GST subunits exist in human which are all in a dimeric form. Based on amino acid sequence similarities, seven classes of cytosolic GST are recognized in mammalian species; Alpha, Mu, Pi, Sigma, Theta, Omega, and Zeta (2–5). As well as being homodimers, the Alpha and Mu classes are also able to form heterodimers so a large number of isozymes are possible from all cytosolic GST subunits (Sinning et al. 1993, LeTrong et al. 2002, Ahmad et al. 1993, Pastore et al. 1998, Tars et al. 2010, Bruns et al. 1999, Balogh et al. 2010, Morel et al. 2002, Li et al. 2005, Patskovsky et al. 2006, Raghunathan et al. 1994, Patskovsky et al. 1999, Comstock et al. 1994, Board et al. 2000, Zhou et al. 2011, Zhou et al. 2012, Sun et al. 2011, Tars et al. 2006, Rossjohn et al. 1998, Polekhina et al. 2001, Inoue et al. 2003). Typical electrophilic substrates are chosen as examples for which the majority of the cytosolic GST isozymes act on.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
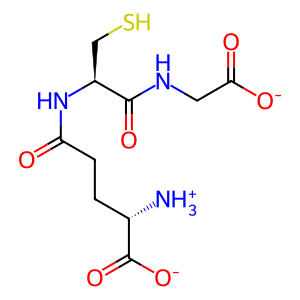
GSH [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-176054
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
glutathionate(1-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-176054