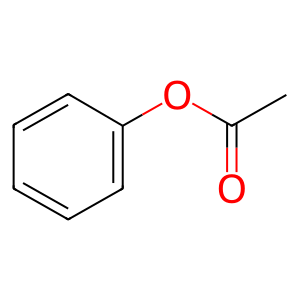
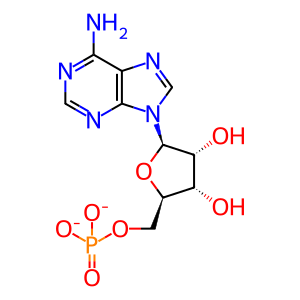
Reaction: phenylacetate + Coenzyme A + ATP => phenylacetyl-CoA + AMP + pyrophosphate
- in pathway: Conjugation of phenylacetate with glutamine
Phenylacetate and ATP react with coenzyme A to form phenylacetyl CoA, AMP, and pyrophosphate (Vessey et al. 1999). Two human CoA ligases have been characterized that catalyze this reaction efficiently in vitro: acyl-CoA synthetase medium-chain family member 1 (BUCS1) (Fujino et al. 2001) and xenobiotic/medium-chain fatty acid:CoA ligase (Vessey et al. 2003). Their relative contributions to phenylacetate metabolism in vivo are unknown.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
AMP [mitochondrial matrix]
PPi [mitochondrial matrix]
phenylacetyl-CoA [mitochondrial matrix]
CoA-SH [mitochondrial matrix]
ATP [mitochondrial matrix]
phenylacetate [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-177157
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
coenzyme A(4-)
ATP(4-)
phenyl acetate
Reaction output - small molecules:
adenosine 5'-monophosphate(2-)
diphosphate(3-)
phenylacetyl-CoA(4-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-177157