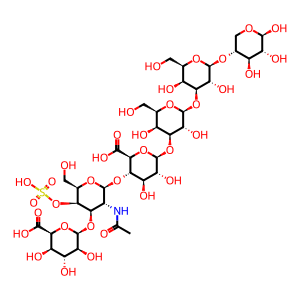
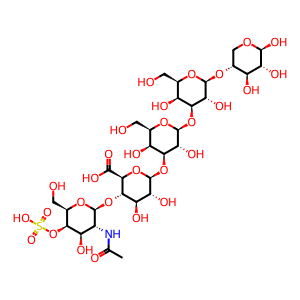
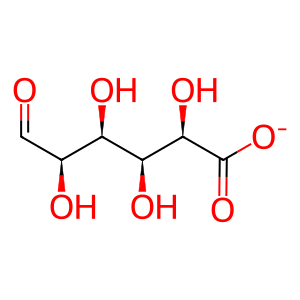
Reaction: IDUA) hydrolyses the unsulfated alpha-L-iduronosidic link in DS
- in pathway: CS/DS degradation
The lysosomal enzyme alpha-L-iduronidase (IDUA) hydrolyzes the nonreducing terminal iduronide glycosidic bond in heparan sulfate and dermatan sulfate (Scott et al. 1991). Defects in IDUA cause mucopolysaccharidosis type IH (MIM:607014, also called Hurler syndrome), mucopolysaccharidosis type IH/S (MIM:607015, also called HurlerScheie syndrome) and mucopolysaccharidosis type IS (MIM:607016, also called Scheie syndrome) (Scott et al. 1993).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
CHEBI:63868 chain [lysosomal lumen]
aldehydo-L-iduronic acid [lysosomal lumen]
H2O [lysosomal lumen]
IdoA-GalNAc(4S)-GlcA-Gal-Gal-Xyl [lysosomal lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1793186
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
beta-D-IdopA-(1->3)-beta-D-GalpNAc4S-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcpA-(1->3)-beta-D-Galp-(1->3)-beta-D-Galp-(1->4)-beta-D-Xylp
Reaction output - small molecules:
beta-D-GalpNAc4S-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcpA-(1->3)-beta-D-Galp-(1->3)-beta-D-Galp-(1->4)-beta-D-Xylp
aldehydo-L-iduronate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1793186