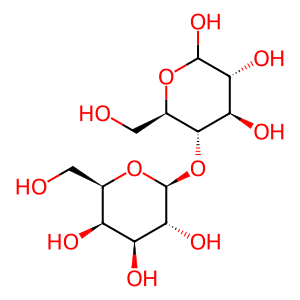
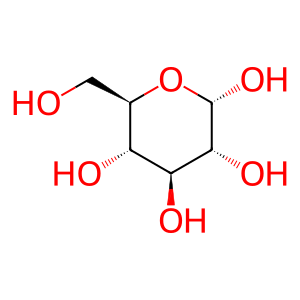
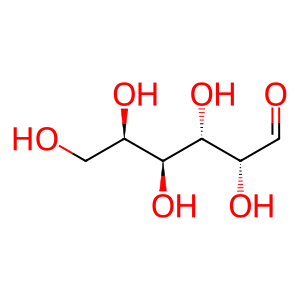
Reaction: lactose + H2O => D-glucose + D-galactose
- in pathway: Digestion of dietary carbohydrate
Extracellular lactose is hydrolyzed to yield molecules of glucose and galactose, in a reaction catalyzed by the lactase activity of lactase-phlorizin hydrolase associated with the plasma membrane. In the body, lactase-phlorzin hydrolase is found on the external face of enterocytes in microvilli of the small intestine (Hauri et al. 1985). Expression of the enzyme is developmentally regulated and subject to a genetic polymorphism: enzyme levels fall after weaning but the extent of the fall varies sharply between human populations (Grand et al. 2003; Swallow 2003). The lactase-phlorizin hydrolase polypeptide undergoes dimerization and two rounds of proteolytic cleavage in the course of its maturation and transport to the cell surface (Grunberg and Sterchi 1995; Wuthrich et al. 1996; Behrendt et al. 2010).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Glc [extracellular region]
Gal [extracellular region]
Lac [extracellular region]
H2O [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-189062
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
lactose
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
alpha-D-glucose
aldehydo-D-galactose
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-189062