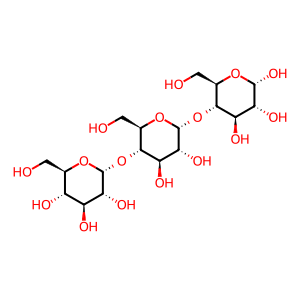
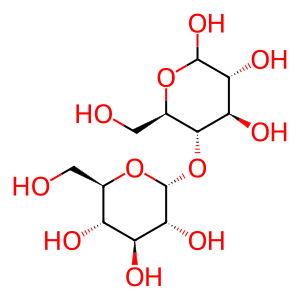
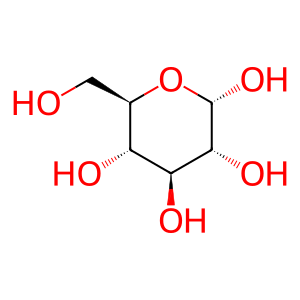
Reaction: maltotriose + H2O => maltose + D-glucose (maltase-glucoamylase)
- in pathway: Digestion of dietary carbohydrate
Maltotriose is representative of linear glucose oligomers containing more than two residues. The 1-4 linkages of extracellular maltotriose are hydrolyzed to yield maltose and glucose in a reaction catalyzed by the exoglucosidase activity of maltase-glucoamylase (Nichols et al. 1998). In the body, this enzyme is found as a dimer on the external face of enterocytes in microvilli of the small intestine (Hauri et al. 1985), and acts on maltotriose derived directly from the diet and from the hydrolysis of starch. This reaction can also be catalyzed by sucrase-isomaltase, but maltase-glucoamylase is about a hundredfold more active.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Mal [extracellular region]
Glc [extracellular region]
H2O [extracellular region]
maltotriose [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-191116
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
alpha-maltotriose
Reaction output - small molecules:
maltose
alpha-D-glucose
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-191116