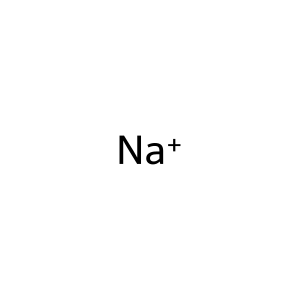Reaction: SLC10A2 transports bile salts and acids and Na+ from extracellular region to cytosol
- in pathway: Recycling of bile acids and salts
A molecule of extracellular bile salt or bile acid (cholate, chenodeoxycholate, or their glycine or taurine conjugates) and a sodium ion are transported into the cytosol, mediated by ASBT (apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter; SLC10A2) in the plasma membrane. In the body, ASBT is expressed on the apical surfaces of enterocytes, and this reaction is the first step in the process by which bile salts and acids are reaborbed from the intestinal lumen and returned to the liver (Kullak-Ublick et al. 2004, Trauner & Boyer 2002). Cytosolic ileal bile acid binding protein (IBABP, FABP6) mediates the transcellular movement of bile acids to the basolateral membrane across which they exit the cells via organic solute transporters (OST) (Kurz et al. 2003). Between the two transport systems (ASBT and OST), ~95% of bile acids and salts are absorbed in the terminal ileum and returned back to the liver via the portal system to be uptaken and resecreted in bile.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Na+ [cytosol]
Na+ [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-194187
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
sodium(1+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
sodium(1+)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-194187