Reaction: C1GALT1 transfers Galactose to the Tn antigen forming Core 1 glycoproteins (T antigens)
- in pathway: O-linked glycosylation of mucins
Glycoprotein N acetylgalactosamine 3 beta galactosyltransferase 1 (C1GALT1; MIM:610555) mediates the transfer of Galactose (Gal) from UDP galactose to single O-linked GalNAc residues (Tn antigens) to form Core 1 structures on glycoproteins. C1GALT1 is active when in complex with the molecular chaperone C1GALT1C1 (aka COSMC; MIM:300611) which assists the folding and/or stability of C1GALT1. Defects in C1GALT1C1 causes somatic Tn polyagglutination syndrome (TNPS; MIM:300622), characterised by the polyagglutination of erythrocytes by naturally occurring anti Tn antibodies following exposure of the Tn antigen on their surface. Defects in C1GALT1C1 render C1GALT1 inactive and results in the accumulation of the incompletely glycosylated Tn antigen. The Tn antigen is tumour associated, found in a majority of human carcinomas, and is not normally expressed in peripheral tissues or blood cells (Crew et al. 2008, Ju et al. 2014). C1GALT1 and C1GALT1C1 belong to the CAZy family GT31 (CAZy.org).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
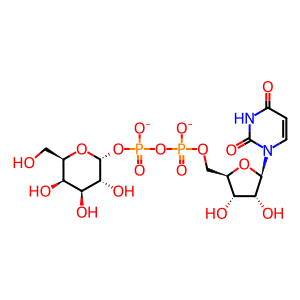
UDP [Golgi lumen]
UDP-Gal [Golgi lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1964505
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
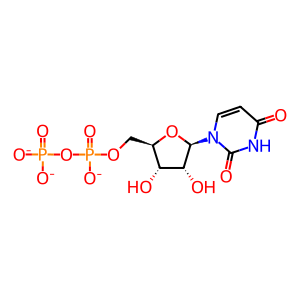
UDP-alpha-D-galactose(2-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
UDP(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1964505