Reaction: IDO1 dioxygenates L-Trp to NFK
- in pathway: Tryptophan catabolism
Cytosolic indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) catalyzes the conversion of L-tryptophan and oxygen to formylkynurenine. The structure and catalytic properties of the human enzyme have been analyzed directly (Sugimoto et al. 2006); the subcellular location and monomeric state of the active form of the enzyme are inferred from the properties of its rabbit ortholog (Shimizu et al. 1976). In the body, IDO is ubiquitously expressed and is induced by interferon. These properties, together with IDO's broad substrate specificity, are consistent with the hypothesis that the enzyme functions functions in anti bacterial and inflammatory processes (Taylor and Feng 1991).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
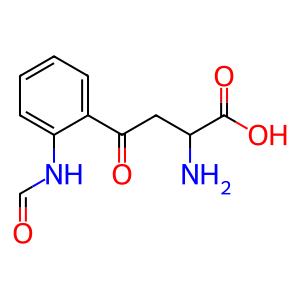
NFK [cytosol]
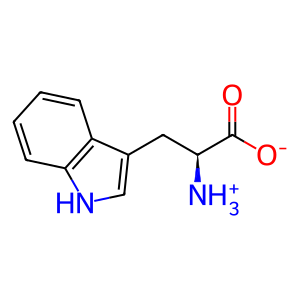
L-Trp [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-198563
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
L-tryptophan zwitterion
dioxygen
Reaction output - small molecules:
N-formylkynurenine
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-198563