Reaction: Mitochondrial FPGS-1 transforms THF to THFPG
- in pathway: Metabolism of folate and pterines
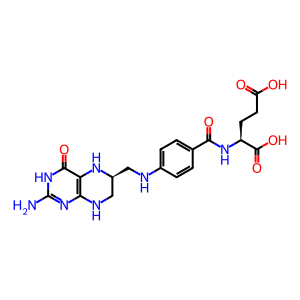
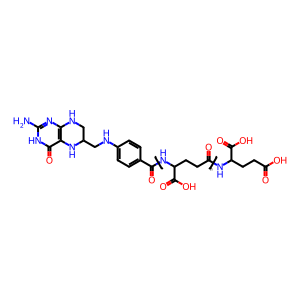
Mitochondrial folylpolyglutamate synthase catalyzes the reaction of THF-glutamate(n), L-glutamate, and ATP to form THF-glutamate(n+1), ADP, and orthophosphate. (The first glutamate residue is attached to the glutamate moiety of THF itself; for convenience the process is annotated here as if it proceeded in a single concerted step.) The extent of conjugation is variable, but the commonest mitochondrial form of THF has six added glutamate residues. Although its properties as a donor of one-carbon units are not affected by glutamate addition, THF that lacks added glutamate residues cannot be retained in the mitochondrial matrix so this reaction is needed for normal THF function under physiological conditions. The mitochondrial and cytosolic forms of folylpolyglutamate synthase are encoded by the same gene - alternative splicing generates mRNA with or without an initial exon encoding a mitochondrial targeting sequence (Garrow et al. 1992; Chen et al. 1996).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Pi [mitochondrial matrix]
ADP [mitochondrial matrix]
THFPG [mitochondrial matrix]
THF [mitochondrial matrix]
ATP [mitochondrial matrix]
L-Glu [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-200682
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
(6S)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolic acid
ATP(4-)
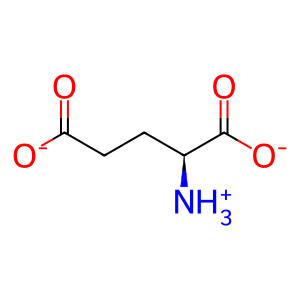
L-glutamate(1-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydrogenphosphate
ADP(3-)
tetrahydrofolyl-poly(glutamic acid) macromolecule
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-200682