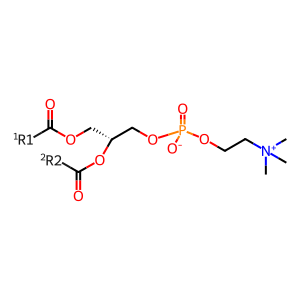
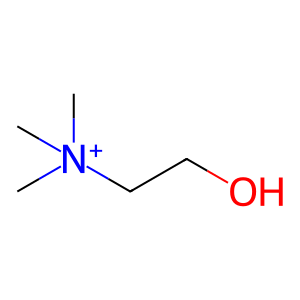
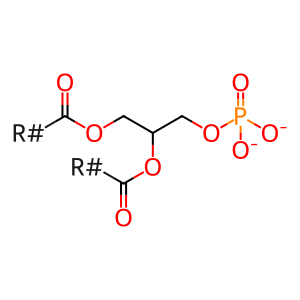
Reaction: Hydrolysis of PC to PA by PLD
- in pathway: Role of phospholipids in phagocytosis
Phospholipase D (PLD) catalyses the hydrolysis of the membrane phospholipid, phosphatidylcholine (PC) to generate choline and metabolically active phosphatidic acid (PA) (Lennartz 1999). Pharmacological inhibition studies show that PLD participates in FCGR-mediated phagocytosis (Kusner et al. 1996). There is an increase in the activity of PLD following the activation of phagocytosis via FCGR (Kusner et al. 1999). Following activation of FCGR, PLD translocates to the plasma membrane at the phagocytic cup and generate PA. This PA can be converted to DAG through the action of phosphatidic acid phosphatase-1 (PAP-1). Thus activation of PLD may be an additional pathway leading to PKC activation.
The two isoforms PLD1 and PLD2 are both shown to be essential for the formation of phagosome at different stages. PLD1 is localized on the endosomal/lysosomal compartment and PLD2 is localized at the plasma membrane. PLD2 may be linked to phagosome formation whereas PLD1 may be involved in the focal exocytosis at the plasma membrane and also in the maturation process (Carrotte et al. 2006).
The two isoforms PLD1 and PLD2 are both shown to be essential for the formation of phagosome at different stages. PLD1 is localized on the endosomal/lysosomal compartment and PLD2 is localized at the plasma membrane. PLD2 may be linked to phagosome formation whereas PLD1 may be involved in the focal exocytosis at the plasma membrane and also in the maturation process (Carrotte et al. 2006).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Cho [cytosol]
PA [plasma membrane]
PC [plasma membrane]
H2O [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-2029471
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
choline
phosphatidate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-2029471