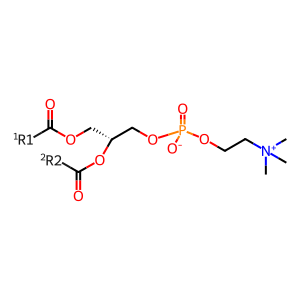
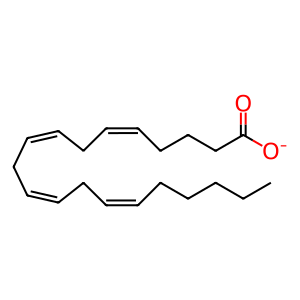
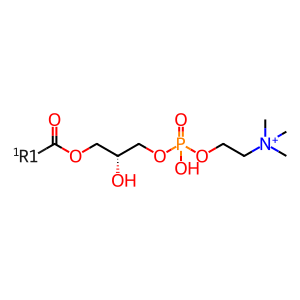
Reaction: Production of AA by iPLA2 upon FCGR activation
- in pathway: Role of phospholipids in phagocytosis
Several members of phospholipase A (PLA) are involved in phagocytosis. Macrophages express three classes of PLA2: secreted Ca-dependent (sPLA2), cytosolic Ca-dependent (cPLA2) and cytosolic Ca-independent (iPLA2) of which iPLA2 is involved in FCGR mediated arachidonic acid (AA) production. Aggregation of FCGR triggers phosphorylation and membrane translocation of iPLA2. Protein kinase C (PKC), ERK and p38MAPK seems to regulate iPLA2 in monocytes, neutrophils and macrophages. Phosphorylated iPLA2 then mediates production of AA and lysoophospholipids from phosphatidylcholine. iPLA2 inhibitors (bromoenol lactone) block AA release and phagocytosis which can be restored upon addition of exogenous AA, suggesting a critical role for iPLA2 in FCGR phagocytosis (Lennartz et al. 1993, Tay & Melendez). Release of AA by activated iPLA2 changes the physical characteristic of the membrane which may facilitate pseudopod extension.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
AA [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
LPC [endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
H2O [cytosol]
PC [endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-2029475
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
Reaction output - small molecules:
arachidonate
1-O-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine(1+)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-2029475