Reaction: Activation of linoleic acid to linoleoyl-CoA
- in pathway: Linoleic acid (LA) metabolism
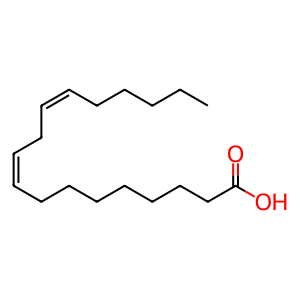
The dietary essential fatty acid (EFA) linoleic acid (LA) is activated to a high energy form known as linoleoyl-CoA by the action of long-chain acyl-CoA synthetases (ACSLs). Thioesterification of long-chain fatty acids into their acyl-CoA derivatives is considered to be the first committed step in fatty acid metabolism. Formation of acyl-CoA allows an otherwise non-reactive fatty acid to participate in biosynthetic or catabolic pathways. This acyl CoA form is converted to its longer-chain polyunsaturated products by a series of desaturation and elongation reactions (Ellis et al. 2010, Watkins 2008).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
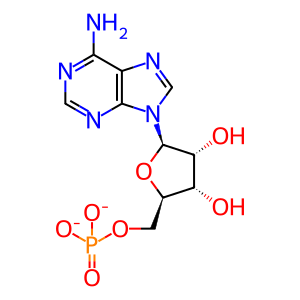
adenosine 5'-monophosphate [endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
PPi [endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
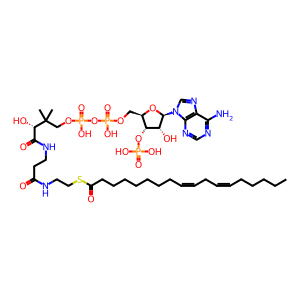
LA-CoA [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
ATP [endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
CoA-SH [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
LINA [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-2046098
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
ATP(4-)
coenzyme A(4-)
linoleic acid
Reaction output - small molecules:
adenosine 5'-monophosphate(2-)
diphosphate(3-)
linoleoyl-CoA
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-2046098