Reaction: NAGLU hydrolyses heparan chain(2)
- in pathway: HS-GAG degradation
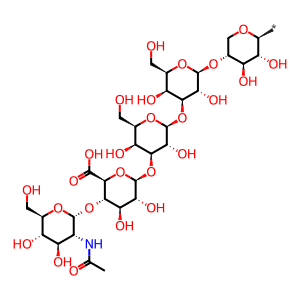
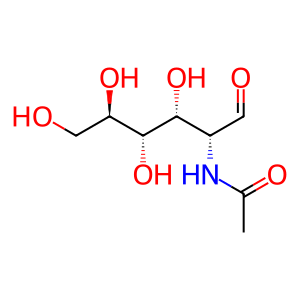
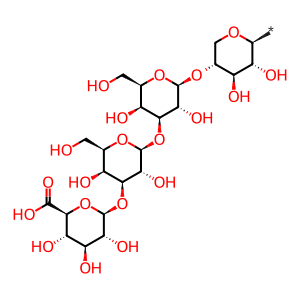
Alpha-N-acetylglucosaminidase (NAGLU) also hydrolyses another non-reducing, terminal N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residue from heparan sulfate. The active form of the enzyme (77kDa) is derived from an 82kDa precursor (Weber et al. 1996). Defects in NAGLU cause Mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIB (MPSIIIB, MIM:252920), also known as Sanfilippo syndrome type B (Beesley et al. 2005).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
GlcNAc [lysosomal lumen]
CS/HS precursor [lysosomal lumen]
H2O [lysosomal lumen]
Heparan chain(2) [lysosomal lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-2090038
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
alpha-D-GlcNAc-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcA-(1->3)-beta-D-Gal-(1->3)-beta-D-Gal-(1->4)-beta-D-Xyl-yl group
Reaction output - small molecules:
aldehydo-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine
beta-D-GlcA-(1->3)-beta-D-Gal-(1->3)-beta-D-Gal-(1->4)-beta-D-Xyl-yl group
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-2090038