Reaction: Dopamine is oxidised to noradrenaline
- in pathway: Catecholamine biosynthesis
Dopamine beta-hydroxylase (DBH; dopamine beta-monooxygenase) is a copper-containing glycoprotein consisting of four identical subunits and catalyzes the oxidation of dopamine to norepinephrine. It requires ascorbic acid as an electron donor. DBH is localized in the norepinephrinergic and epinephrinergic neurons in the central nervous system. The enzyme exists in the secretory vesicles as both soluble and membrane-bound forms. The soluble form is secreted with catecholamines by exocytosis whereas the membrane-bound form is recycled into the vesicles.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
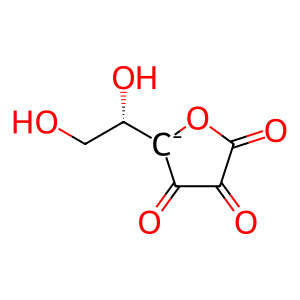
DeHA [secretory granule lumen]
NAd [secretory granule lumen]
H2O [secretory granule lumen]
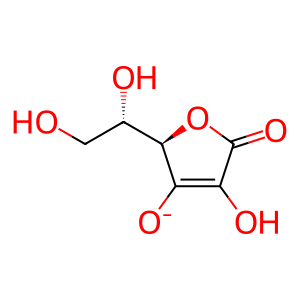
AscH- [secretory granule lumen]
O2 [secretory granule lumen]
DA [clathrin-sculpted monoamine transport vesicle lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-209891
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
L-ascorbate
dioxygen
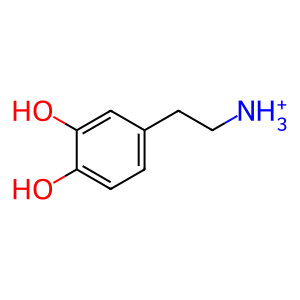
dopaminium(1+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
L-dehydroascorbate
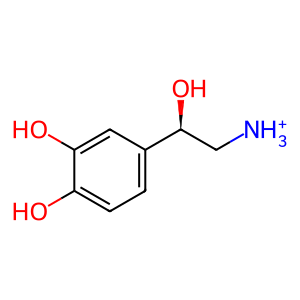
(R)-noradrenaline(1+)
water
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-209891