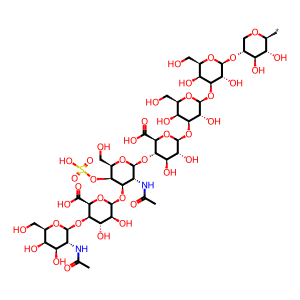
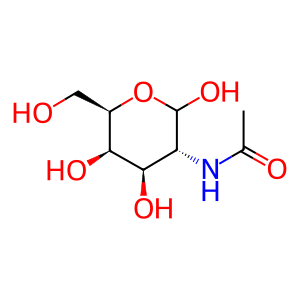
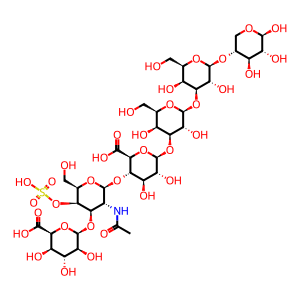
Reaction: HEXA cleaves the terminal GalNAc from DS
- in pathway: CS/DS degradation
Beta-hexosaminidase (HEX) cleaves the terminal N-acetyl galactosamine (GalNAc) from glucosaminoglycans (GAGs) and any other molecules containing a terminal GalNAc. There are two forms of HEX: HEXA and B. The A form is a trimer of the subunits alpha, beta A and beta B. The B form is a tetramer of 2 beta A and 2 beta B subunits (O'Dowd et al. 1988). Defects in the two subunits cause lysosomal storage diseases marked by the accumulation of GM2 gangliosides in neuronal cells.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
GalNAc [lysosomal lumen]
IdoA-GalNAc(4S)-GlcA-Gal-Gal-Xyl [lysosomal lumen]
H2O [lysosomal lumen]
ChEBI:63516 chain [lysosomal lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-2105001
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
beta-D-GalNAc-(1->4)-beta-D-IdoA-(1->3)-beta-D-GalNAc4S-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcA-(1->3)-beta-D-Gal-(1->3)-beta-D-Gal-(1->4)-beta-D-Xyl-yl group
Reaction output - small molecules:
N-acetyl-D-galactosamine
beta-D-IdopA-(1->3)-beta-D-GalpNAc4S-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcpA-(1->3)-beta-D-Galp-(1->3)-beta-D-Galp-(1->4)-beta-D-Xylp
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-2105001