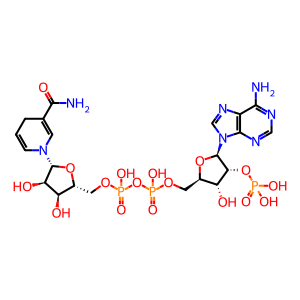
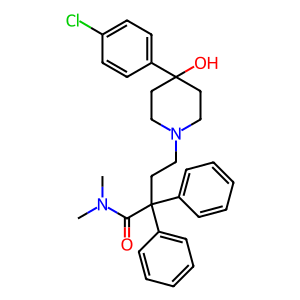
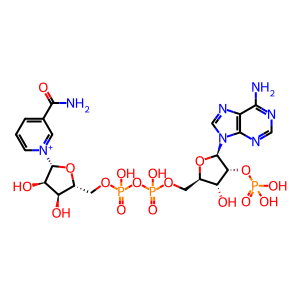
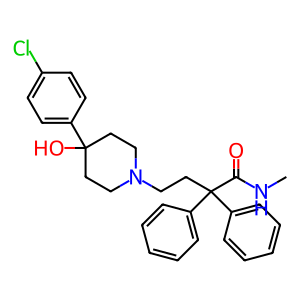
Reaction: CYP3A4 can N-demethylate loperamide
- in pathway: Xenobiotics
The CYP3A family are the most abundantly expressed P450s in human liver, accounting for around 50% of xenobiotic drug metabolism. CYP3A4 is the most abundant member of the family and possesses broad specificity to a range of xenobiotics. Loperamide (LOP), an antidiarrheal, is mainly metabolized to desmethylloperamide (DLOP) through the N-demethylation pathway. This initial N-demethylation is carried out by CYP3A4.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
NADP+ [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
N-demethylated loperamide [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
O2 [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
H+ [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
NADPH [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
LPAM [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-211948
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dioxygen
hydron
NADPH
loperamide
Reaction output - small molecules:
water
NADP(+)
desmethyl loperamide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-211948