Reaction: CYP2U1 19-hydroxylates ARA
- in pathway: Miscellaneous substrates
A novel cytochrome P450, CYP2U1, may play an important role in modulating the arachidonic acid (ARA) signaling pathway. It was discovered by searching the human EST database for homology to existing CYPs and subsequent cloning and expression to obtain the enzyme. CYP2U1 was found to be highly expressed in the thymus and the brain (cerebellum) and found to metabolise ARA to 19-hydroxy-ARA (19HETE) and 20-hydroxy-ARA (20HETE). It is thought that CYP2U1 plays an important physiological role in fatty acid signaling processes in both the cerebellum and thymus (Chuang et al. 1994). The omega-hydroxylation (19) example is described here.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
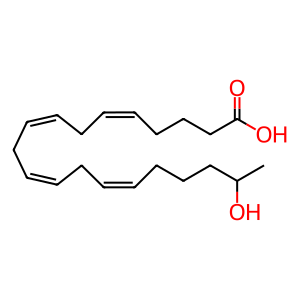
19HETE [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
H2O [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
NADP+ [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
O2 [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
H+ [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
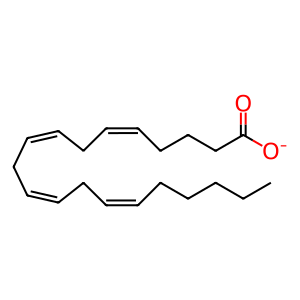
AA [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
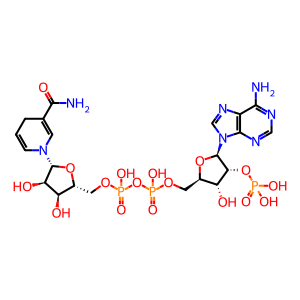
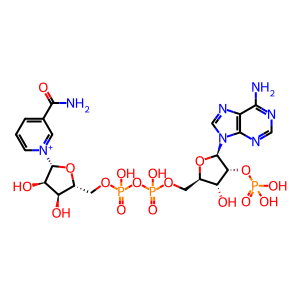
NADPH [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-211960
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dioxygen
hydron
arachidonate
NADPH
Reaction output - small molecules:
19-HETE
water
NADP(+)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-211960