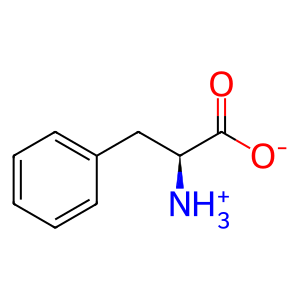
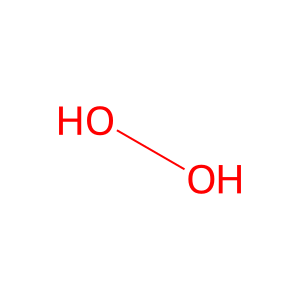
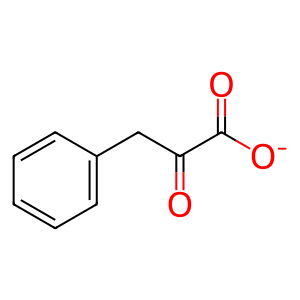
Reaction: IL4I1:FAD oxidises L-Phe to kPPV
- in pathway: Phenylalanine metabolism
Extracellular L-amino-acid oxidase (IL4I1) catalyzes the reaction of phenylalanine, water, and molecular oxygen to form keto-phenylpyruvate, ammonia, and hydrogen peroxide. IL4I1, inferred to form a complex with FAD, has L-amino acid oxidase activity and with a strong preference for phenylalanine. The enzyme, found both in lysosomes and secreted into the extracellular space, is produced in the body by myeloid and dedritic cells (Boulland et al. 2007).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
NH3 [extracellular region]
H2O2 [extracellular region]
kPPV [extracellular region]
H2O [extracellular region]
L-Phe [extracellular region]
O2 [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-2160492
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
L-phenylalanine zwitterion
dioxygen
Reaction output - small molecules:
ammonia
hydrogen peroxide
keto-phenylpyruvate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-2160492