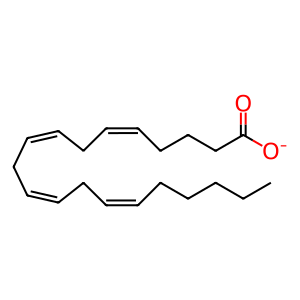
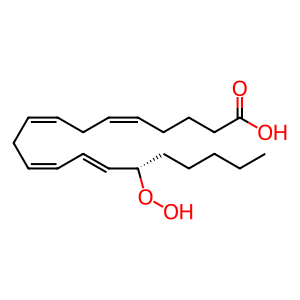
Reaction: Arachidonic acid is oxidised to 15S-HpETE by ALOX15/15B
- in pathway: Synthesis of 15-eicosatetraenoic acid derivatives
Arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase (ALOX15) (Gulliksson et al. 2007, Kuhn et al. 1993, Izumi et al. 1991) and arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase B (ALOX15B) (Tang et al. 2002, Wecksler et al. 2008) are lipid peroxidising enzymes mainly expressed in airway epithelial cells, eosinophils, reticulocytes and in macrophages. They insert molecular oxygen at C-6 from the omega-end of arachidonic acid with formation of the unstable intermediate 15S-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid (15S-HpETE) which can be further converted, enzymatically or non-enzymatically, to 15S-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (15S-HETE).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
15S-HpETE [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
AA [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-2162002
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dioxygen
arachidonate
Reaction output - small molecules:
15(S)-HPETE
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-2162002