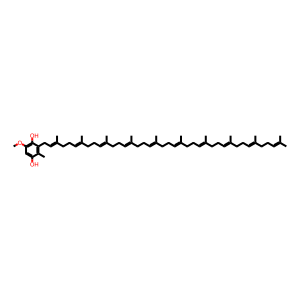
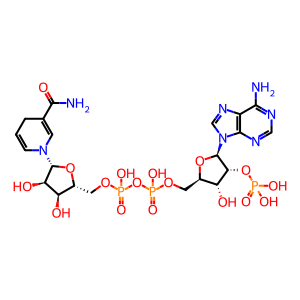
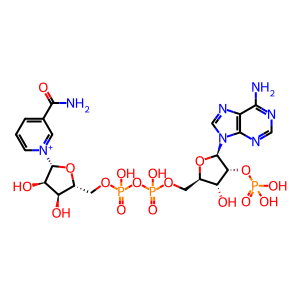
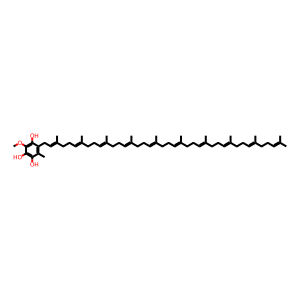
Reaction: COQ9 dimer:COQ7:Fe2+ hydroxylates DMQ10H2 to DeMQ10H2
- in pathway: Ubiquinol biosynthesis
Ubiquinone biosynthesis protein COQ7 homolog (COQ7) (Vajo et al. 1999) catalyses the hydroxylation of 6-methoxy-3-methyl-2-decaprenyl-1,4-benzoquinol (DMQ10H2) to 3-demethylubiquinol-10 (DeMQ10H2). This reaction is inferred from the equivalent reaction in yeast (Marbois & Clarke 1996, Tran et al. 2006). Mitochondrial ubiquinone biosynthesis protein COQ9 is a lipid-binding protein involved in the biosynthesis of coenzyme Q. It binds with COQ7, an interaction that may be necessary to present the lipid to COQ7 activity (Lohman et al. 2014).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
NADP+ [mitochondrial matrix]
DeMQ10H2 [mitochondrial matrix]
H2O [mitochondrial matrix]
O2 [mitochondrial matrix]
DMQ10H2 [mitochondrial matrix]
H+ [mitochondrial matrix]
NADPH [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-2162194
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dioxygen
2-decaprenyl-6-methoxy-3-methylhydroquinone
hydron
NADPH
Reaction output - small molecules:
NADP(+)
3-demethylubiquinol-10
water
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-2162194